Last Updated on February 3, 2024 by Dr. Abadullah Sajid Bashir
What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome, also called IBS, is a neuro-gastrointestinal disorder in which the patient’s digestive system does not function properly. IBS is not fatal, but it causes difficulties in living a normal life due to its changing pattern of symptoms. The major symptoms are abdominal pain, abdominal cramping, constipation or diarrhea, gas, blotting, colon pain, etc. [1]Microsoft Word – Irritable Bowel Syndrome (berkeley.edu)
The causes of IBS are not yet known but it is certain that it has a very deep connection with the brain. If the brain is disturbed, then the chances of developing this disorder are high. Similarly, even if a food is consumed for a long time that is not suitable for the digestive system, then this disorder can also occur.
As a result, a healthy person becomes ill. This disease lasts for a lifetime. This means that once a person has IBS, then it is very difficult to get rid of it. This disorder is widely distributed, and patients of IBS are present all over the world. IBS affects about 20 to 50 million Americans every year. It has been observed that in females IBS is more common.
Although IBS is not life-threatening, but the person cannot live a normal and healthy life. For example, its effects on the study of students, official work of working people, daily home activities, and social life also.
Are there any other names for IBS?
Yes, there are some other names of IBS that are below
- Depressed colon
- Irritable bowel
- Irritable colon
- Nervous stomach
- Spastic colon
- Stressed colon
- Gut-brain disorder
What are the types of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)?
Due to varying the symptoms of IBS, classification has been made. There are five types of IBS. The details are below.
- Irritable bowel syndrome-Diarrhea (IBS-D)
- Irritable bowel syndrome-Constipation (IBS-C)
- Irritable bowel syndrome-Mixed (IBS-M) or IBS-A (alternating)
- Irritable bowel syndrome-Post Infection (IBS-PI) [2] Holten KB, Wetherington A, Bankston L (May 2003). “Diagnosing the patient with abdominal pain and altered bowel habits: is it irritable bowel syndrome?”. American Family … Continue reading
- Irritable bowel syndrome-Unsubtyped (IBS-U)
Irritable bowel syndrome- Diarrhea (IBS-D)
This is a type of IBS when watery stool with mucous come out from the body. Patients who have IBS-D expel an excessive amount of water from the body. Diarrhea in IBS-D leads to dehydration as well as salt deficiency. If a Person consumes normal food, then after some time his/her gut starts to get disturbed, and the patient feels the need to go to the washroom. It seems as if his/her has an infection that has caused diarrhea but is not actually an infection. This is because the digestive system is not taking food normally and is expelling it out from the body. There are other symptoms like pain in the abdomen and gas and mucus also present in this type of IBS. (Watch Video)
Irritable bowel syndrome-constipation (IBS-C)
This is the second and most painful type of IBS in which the patient has constipation, and the stool becomes very hard which makes it very difficult to get it out of the body. The reason behind it is that a large amount of water becomes absorbed in the large intestine which makes the stool very hard, so it becomes difficult to get it out of the body. There is pain, irritation, and discomfort in the abdomen. Similarly, there may be a condition of headache that has also been observed in IBS-C. (Watch Video)
Irritable bowel syndrome-Mixed (IBS-M)
In this type of IBS, the patient suffers from diarrhea and constipation both. This type of IBS is more annoying to the patient. At first the symptoms of IBS-D start when the patient prepares himself to get rid of IBS-D, The IBS-C become starts. And when he tries to get rid of IBS-C, the symptoms of IBS-D start again. This is because the messages from brain that are sent from the brain to digest food do not work normally and as a result, sometimes diarrhea and sometimes constipation occur. (Watch Video)
Irritable bowel syndrome-Post Infection (IBS-PI)
This is the fourth most common type of IBS. In other words, it is a condition in which the symptoms of IBS begin to appear after an infection. Symptoms may begin to appear after a viral, a bacterial, parasitic infection or fungal infection. At first the digestive system will be normal but after attacking some pathogens the GIT become disturbs but it continues this abnormal activity even after ending up the infection. (Watch Video)
Irritable bowel syndrome- Unsubtyped (IBS-U)
Unsubtyped (IBS-U) is a type of irritable bowel syndrome in which symptoms are present, but we cannot say what type of ID it is. If we talk about IBS-D, it includes diarrhea, a special and specific symptom. Similarly, if we talk about IBS-C, then constipation is a special symptom. If we talk about IBS-M, then sometimes there is constipation and sometimes there is diarrhea. Unsubtyped (IBS-U) is a type of IBS that we cannot predict, either it is IBS-C or IBS-D or IBS-M. [3]IBS Unsubtyped – Drossman Gastroenterology, Chapel Hill, NC (drossmancare.com)
What are the symptoms of IBS
The symptoms of IBS are the basic reasons for patient discomfort and anxiety. The following are some of the symptoms.
- Abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Getting diarrhea
- Diarrhea alternating with constipation
- Discomfort in the stomach
- Feeling full stomach
- Feeling more movement in the abdomen
- Flatulence
- Want to pee a lot
- Pain in the colon (Part of large intestine)
- In males, the feeling of discomfort in the left side, the testies due to discomfort in the colon
- Severe cramping in the intestines
- White or yellow mucus in the stool
- Stools come out little by little
- Intestinal pain after defecation
- Feeling that the stomach is not properly emptied after bowel movements
- Gas moving back and forth in the abdomen
- Feeling of discomfort from squeezing the abdomen
In addition to the symptoms described above, some patients have also the following symptoms
- Having a headache
- Having anxiety and depression
- Irregular urination
- Having fibromyalgia
- Back muscles pain
- Weight loss
- Don’t want to have sex
- Feeling bored
- A negative change in attitudes
- Feeling tired
- Emotionally disturbed
Due to the diversity of symptoms of IBS, it can be different from patient to patient. It depends on the subtype of IBS, food consumed, and mental health.
What are the causes of IBS?
The causes of IBS are not yet known, but dysmotility of gut muscles, Brain-gut dysfunction [4]Ohman L, Simrén M (March 2010). “Pathogenesis of IBS: role of inflammation, immunity and neuroimmune interactions”. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 7 (3): 163–173., and Visceral hypersensitivity of nerves could be the basic reasons for IBS. we have not yet reached the root cause of the disease, but it is certain that it can be caused by intestinal infections as well as brain problems and improper functioning of neurotransmitters. Food allergies and genetic factors are also considered for this disorder.
It has been observed that patients who have anxiety and depression etc. also have IBS, which means that IBS is directly related to the brain. Some explanations regarding the causes of IBS are below. [5]IBS.pdf (unc.edu) [6]Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Symptoms, Causes, Treatments, Medications (webmd.com) [7]Symptoms & Causes of Irritable Bowel Syndrome | NIDDK (nih.gov) [8] Wouters MM, Vicario M, Santos J (January 2016). “The role of mast cells in functional GI disorders”. Gut. 65 (1): 155–68. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309151
Disorders of the brain
If the brain is disturbed, then the symptoms of IBS can also start appearing. Similarly, if the stomach is upset then it also affects the brain and the brain starts abnormal information to the gastrointestinal track that could lead to symptoms of IBS. And the disease begins to show its symptoms. [9]Fukudo S, Nomura T, Muranaka M, Taguchi F (September 1993). “Brain-gut response to stress and cholinergic stimulation in irritable bowel syndrome. A preliminary study”. Journal of … Continue reading [10]Spiller R, Aziz Q, Creed F, Emmanuel A, Houghton L, Hungin P, Jones R, Kumar D, Rubin G, Trudgill N, Whorwell P (December 2007). “Guidelines on the irritable bowel syndrome: mechanisms and … Continue reading
Food allergies
Food allergies can also be one of the reasons when the digestive system becomes upset with certain food and it is not able to do its normal activity if it continues like this then it becomes IBS in the future. Similarly, food allergy can trigger the symptoms of IBS [11]https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/4/835/pdf [12]Food allergy in irritable bowel syndrome: The case of non-celiac wheat sensitivity (wjgnet.com)
Having an infection
Infections can also be a major cause of the onset of IBS. If there is any kind of infection in the digestive system i.e., virus [13]Post-infectious IBS: What You Need to Know (mindsethealth.com), bacteria [14]Karolina S Jabbar, Brendan Dolan, Lisbeth Eklund, Catharina Wising, Anna Ermund, Åsa Johansson, Hans Törnblom, Magnus Simren, Gunnar C Hansson. Association between Brachyspira and irritable bowel … Continue reading, fungi [15]Gut fungal dysbiosis and altered bacterial-fungal interaction in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: An explorative study – PubMed (nih.gov) [16]Santelmann H, Howard JM (January 2005). “Yeast metabolic products, yeast antigens and yeasts as possible triggers for irritable bowel syndrome”. European Journal of Gastroenterology … Continue reading, Protozoa [17]Stark D, van Hal S, Marriott D, Ellis J, Harkness J (January 2007). “Irritable bowel syndrome: a review on the role of intestinal protozoa and the importance of their detection and … Continue reading etc. then the digestive system is not able to do its job properly which increases the chances of getting IBS. [18]Barbara G, Grover M, Bercik P, Corsetti M, Ghoshal UC, Ohman L, Rajilić-Stojanović M (January 2019). “Rome Foundation Working Team Report on Post-Infection Irritable Bowel … Continue reading [19]Beatty JK, Bhargava A, Buret AG (April 2014). “Post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome: mechanistic insights into chronic disturbances following enteric infection”. World Journal of … Continue reading [20]Ghoshal UC, Gwee KA (July 2017). “Post-infectious IBS, tropical sprue and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: the missing link”. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & … Continue reading
Use of medicines
If a drug continues to be used for a long time due to an illness, it also affects the digestive system which does not work properly and can cause IBS. [21]MCInfoSheet-IBS[1] (vt.edu)
The use of antibiotics in medicine is noteworthy. If antibiotics are used continuously to eradicate an infection, there is a possibility of IBS. This is because the use of antibiotics also eliminates the good microbiome present in the intestines which affects the digestive system. Similarly, the use of antidepressants and medicines with sorbitol can cause IBS. [22]Hidden Dangers of Antibiotic Use: Increased Gut Permeability Mediated by Increased Pancreatic Proteases Reaching the Colon – PMC (nih.gov)
Vitamin deficiency
A lack of vitamins in the body also affects the normal function of the body, especially the digestive system. Different types of fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins are very necessary for normal activity of overall body metabolism [23]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vitamin. As far as IBS is concerned, a lack of vitamins can also be a factor to start it. For example, Vitamin D deficiency can disrupt the digestive system and can affect the micro-organisms inside the gut as well as the immune system, which in turn develops into IBS. [24]Williams CE, Williams EA, Corfe BM (October 2018). “Vitamin D status in irritable bowel syndrome and the impact of supplementation on symptoms: what do we know and what do we need to … Continue reading [25]Barbalho SM, Goulart RA, Araújo AC, Guiguer ÉL, Bechara MD (April 2019). “Irritable bowel syndrome: a review of the general aspects and the potential role of vitamin D”. Expert Rev … Continue reading
Menstruation in women
IBS is more common in women than in men. It is also thought that one of the main reasons for the high incidence of IBS in women is that they have menstrual periods every month which leads to hormonal disturbance in them. [26]Irritable Bowel Syndrome and the Menstrual Cycle – PMC (nih.gov)
Prolonged fever
Prolonged fever can also be a factor in the onset of IBS. The reason is that fever does not keep the whole body normal. Metabolic chemicals i.e., enzymes in the body do not work properly because the temperature is too high. This does not allow the body’s metabolism to function properly. The same thing is happening with the digestive system and such types of problems i.e., IBS can occur due to the digestive system not working properly due to fever. [27]www.annalsgastro.gr/files/journals/1/earlyview/2019/ev-10-2019-09-AG4742-0428.pdf
Psychological factor
If a person is constantly suffering from anxiety or depression then there is a chance that he/she will get IBS. The reason is that if the brain is not functioning properly then it affects the digestive system. The digestive system will continue to follow these inappropriate signals from the brain which can cause IBS. [28]Li J, Zhu W, Liu W, Wu Y, Wu B (January 2016). “Rifaximin for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials”. Medicine. 95 (4): … Continue reading
Genetic effect
The question is whether genes play a role in the development of IBS. This may be true. The product of this defective gene, protein will not become normal and as a result, that process or function will not be normal and this may be the reason for the onset of IBS. If a gene is responsible for it, it can be passed on from generation to generation. [29]The Role of Genetics in IBS – PMC (nih.gov)
The genetic factor of IBS is not confirmed but it has been observed that in some families, IBS is passed down from generation to generation. And a genetic mutation in a family, the proteins or chemicals, or neurotransmitters produced by the defective gene do not work properly and the symptoms of the disease begin to appear. When it comes to gene mutation SCN5A gene mutation was found in approximately all the IBS patients, which may indicate that it is associated with some form of genetics. [30]Verstraelen TE, Ter Bekke RM, Volders PG, Masclee AA, Kruimel JW (2015). “The role of the SCN5A-encoded channelopathy in irritable bowel syndrome and other gastrointestinal … Continue reading
How to diagnose IBS
Diagnosing IBS is a difficult task because it is a functional disorder. The human digestive system does not function properly, but on the other hand, the digestive system itself is in perfect condition. Similarly, the brain also remains in its normal state, but the brain begins to send abnormal messages to the digestive system that play a key role in disrupting the gut.
X-rays, MRI, CT scans, blood tests, etc., are major sources of normal in diagnosing IBS. Similarly, it is difficult for the doctor to diagnose because the symptoms of IBS can related to other disorders i.e., colon cancer, inflammatory bowel syndrome, stool bleeding or infection, etc. [31]Do published guidelines for evaluation of Irritable Bowel Syndrome reflect practice? – PMC (nih.gov) [32]Chey WD, Kurlander J, Eswaran S (March 2015). “Irritable bowel syndrome: a clinical review”. JAMA. 313 (9): 949–58. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.0954
The most important and understandable way to diagnose is room criteria.
How Rome Criteria beneficial in diagnosing IBS
The most beneficial process in the diagnosis of IBS so far is the Room criteria that can be used to some extent to determine whether a patient has IBS or not.
The three most important steps are involved in Rome criteria in which pain will be observed.
- Either pain is present after defecation
- Either pain is present when changing in defecation frequency
- Either pain is present in the change in consistency of stool
For this, the patient’s symptoms are noticed continuously from one day to one to two months. If the symptoms continue, then it shows that there is IBS. One thing that is important here is that the other diseases may not be present. Diagnostic tests are also performed to check for infections, such as tests for parasitic bacteria, viruses, etc.
Similarly, tests for other disorders such as colon cancer, inflammatory bowel syndrome, hormone disorders, liver disease, etc., may be performed. If tests of said disorders are normal and the symptoms persist, then the patient is thought to have IBS.
Because the symptoms are due to infection can be cured within 15 to 20 days but if the symptoms persist then it can be due to IBS, therefore, the patient is forwarded for further examination. Some more detailed diagnostic tests/procedures are below.
Stool test
The stool test takes a small amount of stool and checks the blood in it, as well as checks the mucus and microorganisms inside it. If it is assumed that the patient has an infection. Similarly, if there is blood in the stool, it is assumed that there is a wound inside the intestines or there is cancer. And it will predict that there is no IBS.
Endoscopy
Endoscopy is also used to find out if there is any disorder other than IBS that causes IBS-like symptoms. For detailed information (Watch Video).
Hydrogen breath test
This test detects the growth of bacteria in the digestive tract. It also looks at the absorption of carbohydrates inside the small intestine. This test looks at the presence of hydrogen gas in the body. This means that there are bacteria in the small intestine that cause IBS-like symptoms. For detailed information (Watch Video).
Biopsy
Biopsy also plays an important role in diagnosing IBS. It is described as taking a small piece of intestinal tissue and then examining it. If there are no ulcers or cancers or inflammatory bowel syndrome inside the intestines that can cause symptoms such as IBS it is perceived that it is IBS. For the process of biopsy (Watch Video).
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is also done, and it is checked whether the digestive system is working properly or not. (How I do it: Ultrasound of the Abdomen – YouTube)
Blood test
Blood tests are also very important in IBS testing. These tests are also done mainly to check the other diseases/disorders in the body to avoid misdiagnosing IBS. Complete blood tests. Hb tests, liver function tests, the presence of organic matter in the blood, etc. can be performed for this purpose.
Tests for food allergies, lactose intolerance, medications, enzyme deficiencies, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease can also be performed to diagnose IBS.
What are treatment options for IBS?
There is no clear cure for this disorder. However, dietary changes, changes in your attitudes and life style, the use of dietary fibbers, and antidepressants can reduce the symptoms.
The doctor’s first advice is to see the patient for himself/herself to see what kind of symptoms are there. Then steps have to be taken to reduce the severity of these symptoms with both a mutual understanding of doctor and patient.
It is also very important because the symptoms of IBS changing and with these changing symptoms the patient has to take steps for himself/herself that can beneficial for him/her.
It is important to note that in the early days of IBS, when the disorder is new to the patient, the patient has to follow the doctor’s advice. But over time, the patient learns from himself what foods to eat and what behaviors to avoid minimizing symptoms.
Here are some tips, how to look or get minimize the IBS
- Food selection
- Lifestyle changes
- Medicines for IBS
- Attitudes and behaviour changes
- Brain Therapies
Food selection
Because IBS is a disorder of the digestive system, it involves the use of highly selected foods. The food that shows the least symptoms. The choice of food also has to be adopted by the patient along with the opinion of the doctor. Similarly, the patient’s own observation is also very important in this regard. [33]WPPC_A_503985_O (ucdavis.edu) Because one type of food may be suitable for one patient but it may not be suitable for another patient and symptoms may appear, so, the patient’s own observation is very necessary. So to make it easier to know which foods cause the least amount of IBS symptoms, a Low FODMAP diet can be used for lowering the symptoms of IBS.
What is FODMAP
It is abbreviated for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols that are short chains of carbohydrate sugars and these sugars have less ability to observe in the small intestine. And in a result, different kinds of symptoms like intestinal cramping, gas, discomfort, diarrhea, and constipation may occur. If IBS patients eat a high FODMAP diet it can lead to IBS symptoms.
What is Low-FODMAP diet chart?
This chart includes a list of foods that contain short-chain carbohydrates that can help in lowering the symptoms of IBS. It is not at all necessary that if one person is getting benefits from this type of food chart but others may not be happy for said.
It varies from person to person. The patient must decide for himself whether he/she has to eat food or not. Similarly, after eating some specific food then observe either symptoms are appearing or not? In general, milk products, wheat flour, Pulses and peas, Onion and garlic, etc. can cause symptoms. You can get a FODMAP diet chart from your doctor or you can download the following one.
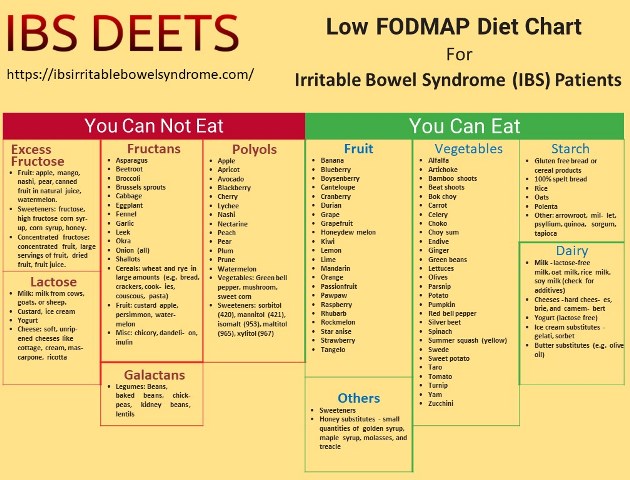
As mentioned above, the symptoms may appear in one patient with eating one type of food but with the same food, symptoms may not occur in another patient.
Lifestyle changes
The most important thing in reducing the symptoms of IBS is that the patient has to change his life and behavior. Here are some suggestions on how to lower your IBS symptoms with lifestyle change.
Eat less
If the food is consumed too much and you have IBS, the symptoms will start to appear. Similarly, if you eat more food, it also increases the chances of gas and cramping. Therefore, it is important to reduce the use of food in IBS.
Exercise and walking
Exercise and walking are very important for patients with IBS. The reason is that by exercising, the brain also tends toward other parts of the body and its attention on the digestive system is reduced to some extent. Similarly, walking and exercise regulate the overall body metabolism of the patient which can lead to lowering the IBS symptoms.[34]gupea_2077_54963_1.pdf;jsessionid=95C7D856A275A2E0C6F06F97098703AA
Exercise also plays an important role in normal bowel movements. Patients who cannot exercise, must walk and walk for at least half an hour. In this way, the food will go to the lower part of the abdomen and in the morning you will be able to leave the washroom easily.
Smoking and alcohol use
Patients with IBS should give up smoking and alcohol use. Doing so will improve their body metabolism which will help in reducing the symptoms of IBS.
Interacting people and making friends
People who suffer from IBS and are living a lonely life should end their loneliness by connecting with new people and sharing their thoughts with them and trying to solve their problems. There will also be peace of mind and it will have an effect on reducing the symptoms of IBS.
Make your own food chart
It is very important for the IBS patient to make a list of their diet and write down the details of the diet according to the season and time, which foods show the symptoms, and which do not. And then follow these written instructions. However, it will be much easier to minimize IBS symptoms in every season.
Some behavioral changes can also trigger the IBS symptoms like traveling and headache, domestic anxiety and stress, overwork Burdon, breakups in relations, etc. so you have to avoid said.
Medicines for IBS
As far as the use of medicines is concerned, it should be used very carefully and with the advice of your doctor.
The unnecessary use of drugs can cause harm rather than a benefit. Below are some types of medications that can be used to reduce the symptoms of IBS.
- Natural treatment for IBS
- Use of peppermint
- Antibiotics
- Antidepressants
- Antispasmodic drugs
- Anticholinergic drugs
- Drugs for constipation in IBS
- Drugs for Diarrhea in IBS
- Antiulcer drugs
- Antipsychotic drugs
- Medicines for acid reflux in IBS
Natural treatment for IBS
Natural food and products that support the digestive system are very important in IBS. The most important of these is the fiber in the diet. Psyllium husk can also be used as natural fiber. Similarly, for roasted barley at night, using roasted corn can also be beneficial. Similarly, other foods containing a large amount of fiber help in normalizing the digestive system which also reduces the symptoms of IBS. Different types of plant and animal content are available as a treatment options for IBS in different areas of the world. i.e., Unani medicine, Chinese medicine, Indian local medicine, etc. The patient has to review first before taking such kinds of local products that have not been checked through the medical research process. One more important thing that result of every diet content may be different patient to patient so, read literature before consumption of any type of food content.
Use of peppermint
Peppermint fresh or its oil capsules also play an important role in reducing the symptoms of IBS. The digestive system is energized and refreshed by using said. Because it is a natural plant, it does not have a lot of side effects and some desired results can be achieved if consumed in balance dose. [35]Peppermint oil for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome | American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy | Oxford Academic (oup.com)
Medication is used only after seeing the symptoms and cannot be taken without a doctor’s advice. Now there are various symptoms of IBS as mentioned above. Medications are used to keep these symptoms in mind.
Use of antibiotics
Antibiotics are used if there is a bacterial infection and IBS-like symptoms begin to appear in the digestive system. Medicine is used for two weeks to six months, depending on the type of infection.
Rifaximin is a popular antibiotic that is used to treat bacterial infections. [36]Rifaximin in irritable bowel syndrome: rationale, evidence and clinical use – PMC (nih.gov)
The following is a list of antibiotics that are used to kill bacteria in IBS.
- Clarithromycin
- Metronidazole
- Neomycin
- Rifaximin
Antidepressant use in IBS
These are medicines that are used to treat anxiety and depression. In the case of IBS, doctors can prescribe antidepressants. when the patient is suffering from some kind of anxiety and depression and because of this he/she is showing symptoms of IBS. [37]Antidepressants for irritable bowel syndrome—A systematic review – ScienceDirect Never do this without consulting a doctor. Because its side effects can be harmful to health.
The following is a list of some antidepressants that have been shown to be effective in treating IBS.
- Citalopram
- Escitalopram
- Escitalopram oxalate
- Fluoxetine
- Fluvoxamine
- Paroxetine
- Sertraline
- Vilazodone
- Vortioxetine
Use of antispasmodic drugs in IBS
Antispasmodics are drugs that help control or normalize the movement of the intestines, especially the colonic muscles. This means that if symptoms of IBS are appearing and accompanied by pain in the colon, the doctor may recommend the use of an anti-spasmodic drug. Which, can help in relaxing the intestine. [38]en_0120-9957-rcg-34-03-00269.pdf (scielo.org.co)But on the other hand, it is also a fact that anti-spasmodic drugs have side effects that can lead to problems in the future. [39]Antispasmodic – an overview | ScienceDirect TopicsSo, these medications can only be used with a doctor’s consent.
Following list of drugs that can be used to normalize the movement of the intestines in IBS
- Alverine citrate
- Chlordiazepoxide
- Clidinium Bromide
- Mebeverine
- Otilonium bromide
- Phloroglucinol
- Pinaverium Bromide
Anticholinergic drugs for IBS
These drugs are used to reduce acetylcholine activity. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that acts as a communicator with the brain and smooth muscles.[40]acetylcholine | Definition, Function, & Facts | Britannica The high amount of acetylcholine leads to high activity of muscle action. Now in the case of IBS if more acetylcholine is released more intestinal activity may occur. So, it can lead to abdominal cramping which is a symptom of IBS. So, a normal level of acetylcholine is required for intestinal function, [41]Neurotransmitter Dysfunction in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Emerging Approaches for Management – PMC (nih.gov) if it is enhanced then the doctor can prescribe one of the following anti Anticholinergic medicine.
Following list of drugs that can be used to normalize the neurotransmitter/Acetylcholine in IBS
There are some other kinds of drugs that are also present to treat different symptoms of IBS. Doctor can prescribe according to need of different types of IBS.
Drugs for constipation in IBS
Following list of drugs that can be used to eliminate constipation in IBS
Drugs for Diarrhea in IBS
Following list of drugs that can be use to eliminate Diarrhea in IBS
Antiulcer drugs
If some kind of ulcer present in gastrointestinal track, than doctor can prescribe the specific antiulcer drugs.
Following list of drugs that can be used to eliminate ulcer in IBS patients.
- Cimetidine
- Dexlansoprazole
- Esomeprazole
- Famotidine
- Isopropamide
- Lansoprazole
- Nizatidine
- Omeprazole
- Pantoprazole
- Rabeprazole
- Ranitidine
Antipsychotic drugs
Antipsychotic drugs are used to treat psychological disorders like Schizophrenia, Schizoaffective disorder, Dementia, Tourette syndrome, Bipolar disorder, irritability in autism spectrum disorder. In some cases, the person having some kind of psychological disorders may be leads to the symptoms of IBS. Or on the other hand IBS patient may have some kind of psychological issues. So, in that case doctor can prescribe some antipsychotic drugs to IBS patients. It is very necessary and important antipsychotic drugs can only be used after detail discussion with your doctor.
Following list of drugs that can be used to treat psychological disorders in IBS patients.
Medicines for acid reflux in IBS
Acid reflux is abnormal functionality of gastrointestinal track by which stomach acid come back up to the esophagus that can cause heart burn in the person. In the case of IBS patient heart burn may occur due to acid reflux. Your doctor can prescribe anti acid reflux drug to the patient.
Following list of drugs that can be used to treat acid reflux in IBS.
Use of probiotics
Probiotics are living bacteria that are like the bacteria in a normal gut. Bacteria inside the gut play an important role in keeping the system functioning. Probiotics are used for IBS patients who support the digestive system and help it function normally. [42]en_0120-9957-rcg-32-02-00141.pdf (scielo.org.co)
Probiotics should not be used without a doctor’s advice. Most important probiotics that can present in normal gut are Bifidobacterium animalis, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium infantis, Bifidobacterium lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus etc. Doctor can prescribe probiotics for your IBS.
Therapies for IBS
If a patient is experiencing symptoms related to IBS due to a particular mental disorder then immediate resolution of his mental disorder is very important. For this the doctor decides according to the need of the patient which may some kind of psychotherapy, physical therapy is needed. Depending on the cause, one or more of the following therapies may be adopt.
Cognitive behavior therapy
This therapy helps the patient to get out of the emotional condition in which he/she is present, due to which he/she is showing symptoms of IBS. If the patient is able to get out of them. So the symptoms of IBS due to anxiety can be reduced. For details Watch Video
Hypnotherapy
This therapy is also a type of hypnosis in which the focus is kept and the desired results are achieved. Gut-hypnosis is performed in the case of IBS. The gut is regularized and the focus is placed on the gut to reduce the symptoms of IBS. For details Watch Video
Mind relax therapy
If IBS is caused by a brain disorder or an emotional disorder, a doctor can suggest the
Mind relax therapy. In mind relax therapy there are serval things that can be considered i.e., breathing, listening music, nature side visit, fishing, hunting, recreation etc. It is also depend on nature and interest of patient.
In this, psychiatrists devise a mechanism by which the brain relaxes and the brain is attracted to normal function and the symptoms of IBS are reduced. For details Watch Video
Biofeedback therapy
This therapy is used to treat IBS. The patient is trained to control his involuntary actions that are taking place in the body to some extent. Similarly, when the symptoms of IBS become severe. Attempts are made to normalize these symptoms without medication. [43]Biofeedback for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome – PMC (nih.gov) For details Watch Video
Acupuncture therapy
Acupuncture therapy can also be prescribed by a doctor, which does not use medicine but tries to reduce the symptoms of IBS with acupuncture.
This is a procedure in which very fine needles are inserted into the body and moved in a certain direction to reduce the symptoms of IBS. [44]IBS Alternative Treatments: Acupuncture, Herbs, and Supplements (webmd.com) For Details Watch Video
Important: IBS is not life threatening but you have to seek knowledge how to live with it.
Thanks for reading this article. For any suggestions you can contact with us.
This article has written after deep scientific/research based study and published after reviewed by health experts. Details are below.
Written By:
- Dr. Abadullah Sajid Bashir
Reviewed By:
- Dr. Muhammad Zubair Chaudhary
- Dr. Muhammad Khan Malik
For Reviewer Details Click Here
References

1 thought on “Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) : Complete information”